Hemorrhoids - a disease associated with varicose inflammation and swelling of the veins of the rectum in the anus. Affected areas protrude outwards, they can form large nodules (protrusions) that interfere with the promotion and exit of feces. The disease affects men and women, it is dangerous for bursting veins, adding a secondary infection.
Classification of hemorrhoids
Depending on the location of the pathological site, there are 2 types of disease:
- External. The veins on the anus, which are covered with skin, become inflamed. This makes it harder to damage the affected areas, they have stronger "protection". Discomfort during defecation is less, but often creates unpleasant friction from the bedding. Complications of external hemorrhoids occur less frequently, are easier to treat.
- Interior. The affected veins are located in the rectum above the anus, which makes it difficult to determine the early stage of the disease. Vessels are covered with thin epithelium, so they are more susceptible to mechanical damage. The internal form of the disease often becomes chronic, is more dangerous with complications, more difficult to treat.
According to the severity of the flow, internal hemorrhoids are divided into 3 stages (stages):
- Initial (1). Nodes protrude, bleed, but do not fall out.
- Moderate (2). With muscle tension (during defecation, exercise), swollen veins come out of the anus. When everything relaxes, they come back.
- Heavy (3). Knots fall out, even when there is no muscle tension, they do not recede on their own.
Symptoms
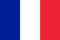
The main signs of hemorrhoids are bleeding from the anus, pain with tension in the muscles of the rectum. The complete picture depends on the stage of the disease. If nodules appear (separate swollen parts of the veins), they look like nodules of dark pink or purple (rarely almost black) color, easy to feel and dense. The nuance depends on the filling of the veins: if blood clots have formed, the blood has collected and cannot come out, the nodules will be dark.
internal hemorrhoids
In the first days and weeks the disease hardly manifests itself. It begins with edema that is not felt if the rectum is not probed from the inside. There are no pain receptors in that part, so the person does not feel discomfort, even during the defecation process.
In the early phase of hemorrhoids, you can find out about its existence only by the drops of blood that appear after the release of large and hard feces. Due to edema, the walls of the rectum narrow the lumen, the mucosa is more damaged during constipation. Important - with hemorrhoids, almost every bowel movement causes a small amount of blood to appear.
Other symptoms will follow:
- Pain during bowel movements. Severe swelling will cause muscle spasms, and even soft stools will cause discomfort.
- Burning, itching. Inflammation in the rectum produces a lot of mucus that irritates the tissues.
- Blood. It appears in large numbers when nodules form. Important: hemorrhoids are bright red - not dark.
- drop the knots. They appear in the last stages of hemorrhoids. First, they pull themselves back, and then they have to "push" with their finger.
External
The external veins are covered with skin, which has many pain receptors. Already in the early stage of hemorrhoids a person will feel discomfort if the veins are swollen. Pain occurs during defecation, both when wiping the anus and when the bedding is in firm contact with the skin. If the inflammation is severe or a blood clot forms in a vein, a large bump forms. Easy to touch, touch causes pain.
Skin with external hemorrhoids becomes sensitive, often shrinking due to swelling. The process of cleaning the anus after defecation is difficult, so the risk of secondary infections increases. Blood then appears if the hemorrhoids are damaged, but it will be less than when creating internal cones.
Causes
The disease is associated with impaired blood flow in the veins of the rectum, which is often caused by congestion in the pelvic organs. Due to them, the pressure in the veins that swell and protrude increases. In most people, this happens due to improper lifestyle and diet, but doctors do not rule out the influence of heredity, genetic vascular anomalies and increased blood clotting.
Possible reasons for the appearance of hemorrhoids:
- Frequent constipation - leads to tension in the veins of the anus, damage to the mucous membrane during the promotion of solid feces.
- Diarrhea - acute and chronic.
- Pregnancy - causes swelling, causes pressure of the growing uterus on the rectum.
- Hormonal fluctuations - cause atony of the pelvic floor muscles.
- Intestinal oncology (more often - colon).
- Delayed operations on the rectum, less often - on the pelvic organs.
- Spinal cord injury, curvature of the spine, injuries of the lower back, sacrum, buttocks.
Additional risk factors:
- Sedentary lifestyle - causes blood stagnation in the pelvis.
- A low-calorie, low-fiber diet causes constipation.
- Lifting weights causes muscle tension.
Diagnosis
The doctor examines the anamnesis and asks clarifying questions to rule out other causes of anal bleeding. Hemorrhoids are similar in symptoms to tumors in the digestive tract, polyps, anal fissures, mucosal prolapse.
After the doctor performs a rectal examination, feeling the lower part of the rectum with your finger. In the early stage of internal hemorrhoids, this may not give results, and in the later phase, the procedure will be delayed if the swelling is very strong and the patient's touch causes acute pain. In order to clarify the diagnosis and a more detailed examination of the anus, examinations are performed by a surgeon or gastroenterologist.
The following methods are used:
- Anoscopy. Examination of the rectum up to 10 cm from the anus. The procedure is painless, but some patients are given local anesthesia (gel, spray).
- Sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy. The tube is inserted into the patient's colon to rule out other causes of bleeding (tumors) and suspected lesions in the upper parts.
- MRI. Tomography is performed if it is not possible to make an accurate diagnosis based on other procedures.
Laboratory research
Blood tests are rarely prescribed, it depends on the clinical picture of the disease. This is necessary if a secondary infection has occurred in order to identify the pathogen. They also do analysis in situations where rectal bleeding is abundant to see hemoglobin level, number and activity of red blood cells. The main diagnosis does not require laboratory procedures.
Treatment
If there are no symptoms of the disease, no special therapy is needed. Your doctor will advise you to change your lifestyle and diet so that hemorrhoids do not develop, the stool becomes softer and does not injure inflamed or swollen mucous membranes. The patient will be offered to move more, to do gymnastics aimed at developing the muscles of the "lower press" and the small pelvis.
How to treat hemorrhoids, which cause discomfort, is determined by the doctor, considering the stage of the disease. In the early stages, it is really only possible to manage medications. If there are many nodules, they are thrombosed and do not recede on their own, surgery may be needed. In any situation after the patient should adhere to the recommendations on diet and lifestyle, because 50% of cases have a relapse. The exception is surgery: after it, repeated hemorrhoids occur in only 5% of patients.
Diet
The tasks of nutrition are to save a person from constipation, to prevent the development of inflammation. Fiber sources are included in the diet: vegetables, herbs, fresh fruits. Carefully handle cereals, especially rice - they can make the stool thick. In addition, they drink more clean warm water: it does not allow feces to sinter, and also speeds up the process of cleaning the intestines. Simple carbohydrates and sugar should be discarded so as not to cause inflammation.
Medical therapy
- Laxatives. Preparations that soften the stool and relieve constipation, prevent new damage to the mucous membrane. They are drunk carefully so as not to cause loss of intestinal muscle tone and diarrhea.
- Candles with anesthetic. Relieve pain in internal hemorrhoids.
- Vasoconstrictor. This is also a local therapy that reduces swelling.
- Anticoagulants. Stop the bleeding.
- Hormonal preparations. They are used topically (injections) for severe inflammation.
Surgical intervention
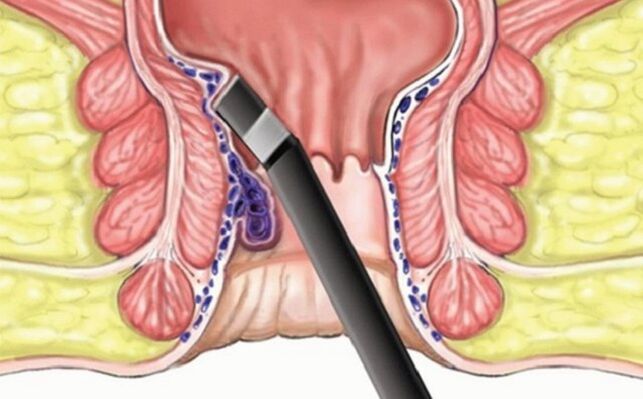
In the last stage, hemorrhoids require surgery:
- Ligation. An instrument is inserted into the anus, which pushes the latex ring over the knot and tightens it. The affected area disappears after 3-4 days.
- laser surgery. The procedure with minimal trauma is almost painless, but there are many contraindications.
- Classical hemorrhoidectomy. The nodules are removed with a scalpel or a special device that then "sews" the edges of the mucosa. If necessary, the doctor removes blood clots.
Alternative medicine
The initial stage of external hemorrhoids includes symptomatic therapy:
- Warm baths. They are made from marigold, chamomile, sage. These herbs relieve inflammation, muscle spasm. They sit in baths for 20 minutes to 2-3 times a day.
- Compresses. With grated raw potatoes, aloe juice, chamomile decoction, buckthorn oil. They are left on the gauze for 30-60 minutes.
Prevention
To avoid the question of how to cure hemorrhoids, follow simple rules:
- Move more. When sitting, get up every 1-2 hours for 5-10 minutes. Walking in the fresh air, choosing stairs instead of an elevator, the possibility of walking a few meters on foot, not driving a car.
- Watch your diet. Eat more plant foods, maintain water balance, do not abuse bread and complex carbohydrates - cereals, pasta.